The Earth’s lithosphere isn’t just one solid piece. It’s made up of about a dozen major plates and several minor ones. These tectonic plates form the Earth’s surface and are always moving. Their movement, known as plate motion or tectonic shift, happens because of heat from the Earth’s mantle.
Key Takeaways:
- Tectonic plates are in constant motion due to various forces acting upon them.
- Plate motion, also known as tectonic shift, is caused by the heat generated by radioactive processes in the Earth’s mantle.
- This movement shapes the Earth’s surface over long periods of time.
- The study of tectonic plate movement helps us understand geological phenomena like earthquakes and volcanic activity.
- Plate movement is driven by mantle convection currents, ridge push, and slab pull forces.
The Earth’s Interior and Plate Movement
The Earth has various layers inside it, each unique in its own way. At the very top, we find the lithosphere. It includes the crust and part of the mantle below. This layer is stiff and broken into tectonic plates that constantly move.
These tectonic plates move because of plate tectonics. This process is fueled by heat from the Earth’s mantle. As radioactive elements break down, they release heat. This makes the mantle’s material warm and light, which causes it to move up toward the lithosphere. This movement makes the plates shift.
Where plates meet, big changes happen. At divergent boundaries, like mid-ocean ridges, plates drift apart. Here, magma comes up and forms new crust. At convergent boundaries, plates crash into each other. One slides under the other, causing volcanoes and mountains. Transform boundaries have plates sliding side by side, often causing earthquakes.
To truly understand earthquakes, volcanoes, and how new landforms appear, we need to know about the Earth’s interior and tectonic plates. Geologists look at plate tectonics to learn about our planet’s dynamic changes and its evolving surface.
Key Points:
- The Earth’s interior includes the lithosphere, which has the crust and part of the mantle.
- The lithosphere is made of tectonic plates that are always moving.
- The movement of these plates is caused by heat from radioactive processes in the mantle.
- Most geological activities happen at plate boundaries, like creating new crust, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes.
- Learning about plate tectonics allows scientists to understand Earth’s changing nature and geological processes.
The Breakup of Pangaea and Continental Drift
Long ago, the Earth looked very different with a supercontinent called Pangaea. Pangaea had most of the planet’s land. Surrounding it was Panthalassa, a huge ocean. This old Earth setup was very different from what we know now.
The breaking of Pangaea led to our current continents. This happened because of continental drift. It occurs due to the movement of tectonic plates beneath the Earth.
Continental drift shows how Earth’s land has moved over time. Alfred Wegener, a German expert, introduced this idea in the 1900s. He suggested all continents were once joined together but later separated.
Wegener used fossils and rocks to support his continental drift theory. But, his ideas weren’t accepted until much later. That’s when scientists really started to understand it.
Pangaea broke apart because of tectonic plates moving. These plates make up Earth’s crust. They lie on a semi-liquid layer underneath.
The heat inside the Earth creates movement in this semi-liquid layer. This movement causes the plates to shift. Thus, continents change positions.
“The tectonic plates act like puzzle pieces that can fit together or slide apart.”
Over many years, heat made Pangaea split into smaller continents. This is how we got the continents and oceans we see today.
Continental drift led to amazing land and sea forms. For instance, South America and Africa’s coastlines match up perfectly. This shows they were once connected.
Here’s how Pangaea split and what it created:
| Continental Breakup | Resulting Land Masses | Ocean Basins Formed |
|---|---|---|
| Pangaea splits into Laurasia and Gondwana | North America, Europe, and Asia came from Laurasia. South America, Africa, and others split from Gondwana. | Atlantic Ocean forms between Laurasia and Gondwana (now North America and Africa) |
| Gondwana fragments further | Australia split from Antarctica. India moved north to Asia. | Indian Ocean forms between India and Africa |
The breakup of Pangaea and drift changed Earth a lot. It affected where plants, animals, and resources are found. Studying this helps scientists learn about Earth’s history and how it changes.
Next, we’ll look at how fast plates move and what happens because of that.
Rates of Plate Movement and Geological Consequences
Tectonic plates are always moving, averaging about 1.5 centimeters (0.6 inches) each year. But, the speed can change based on location. For instance, in coastal California, plates move quicker at nearly 5 centimeters (2 inches) per year.
This fast movement has many effects on the Earth’s surface. One major effect is frequent earthquakes in areas with higher plate movement. When plates meet, they grind together, causing seismic activity.
Earthquakes can range from small tremors to large ones that cause a lot of damage. We measure earthquakes with the Richter scale, which shows how much energy is released. A higher number on the scale means a stronger earthquake.
Besides earthquakes, high plate movement can also cause volcanoes to erupt. When plates push together or pull apart, it can start volcanic activity. Magma from below the Earth comes up through vents and erupts. This eruption brings out gases, lava, and ash.
Volcanoes can explode or just flow, depending on the magma and gases. Explosive ones throw out ash and rocks, while flowing ones gently release lava. Both types change the environment around them, destroying plants and changing the land.
The speed at which plates move and its effects are crucial to studying Earth. Knowing about plate movements helps us understand earthquakes, volcanoes, and the Earth’s landscape. It also shows us where natural resources might be and the risks for people living nearby.

The ongoing shift of tectonic plates molds our planet’s surface. By examining plate movements and their outcomes, scientists learn more about Earth. This knowledge helps them find ways to lessen the dangers from earthquakes and volcanoes.
Convection and Plate Movement
The cause of plate movement is complex and not fully known. Yet, many experts think convection in the mantle is key. Convection means the heat transfer by moving heated fluids. Inside Earth, convection cells in the mantle heat up. This makes solid rocks move up towards the crust while colder rocks sink towards the core. Scientists believe this convection pushes the tectonic plates, but they’re still figuring out how.
Some scientists think that convection currents in the mantle push the plates. As the mantle heats up, hot areas rise, and cool areas sink. This makes a circular motion, like stirring a pot of soup. These currents can move the plates towards, away from each other, or make them slide past each other.
But, convection isn’t the only thing that moves plates. The Earth’s internal heat, including heat from radioactive decay, also helps drive convection. The way the lithosphere resists, how tectonic plates interact, and the asthenosphere’s influence also matter to plate movement.
“Convection in the mantle is a fascinating process that contributes to the dynamic nature of our planet. While we continue to unravel the intricacies of plate tectonics, understanding the role of convection is key to comprehending the forces that shape our Earth.”
Current Research and Future Insights
Researchers are exploring how convection relates to plate movement to learn more about Earth’s dynamics. They use things like seismic imaging and numerical modeling to get a better grasp of convection’s effects on plate tectonics.

This image shows how heat moves in Earth’s mantle. It suggests this movement could be what moves the tectonic plates.
Three Forces Behind Tectonic Plate Movement
There are three main forces that help move tectonic plates. Understanding these forces helps us know how our planet’s surface changes. Let’s look closely at each one:
Mantle Convection Currents
One key force is the movement of mantle convection currents. In the Earth’s mantle, warm currents move like a belt, carrying heat. This motion helps move the tectonic plates. As hot material goes up and cool material goes down, it creates a cycle. This cycle of molten rock moves the plates in different directions.
Ridge Push
Ridge push also moves tectonic plates. It happens at mid-ocean ridges where the Earth makes new lithosphere. This process forms a high ridge, lifting the plates. Then, the plates push away, moving the earth’s crust.
Slab Pull
Slab pull is another strong force. It happens when heavy, old plates sink into the mantle at subduction zones. Gravity pulls these plates down, dragging the rest with them. Slab pull is very strong in these zones. It also causes earthquakes and volcanic activity.
To wrap up, mantle convection currents, ridge push, and slab pull drive the tectonic plates. These forces work together and change the Earth’s landscape. They cause earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountains. The movement of plates shows how connected and complex our Earth is.
| Forces | Driving Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Mantle Convection Currents | Warm currents act as a conveyor belt, propelling the tectonic plates. |
| Ridge Push | Newly formed plates push away the surrounding lithosphere due to their higher elevation at mid-ocean ridges. |
| Slab Pull | Older, denser plates sink into the mantle, pulling the rest of the plate along with them. |
The Influence of Gravity on Plate Movement
Gravity is key in moving tectonic plates. It works with three forces: mantle convection currents, ridge push, and slab pull. These forces drive the plates, changing the Earth’s surface. One big result is subduction, where oceanic plates go under others.
Subduction happens when two plates meet and the heavier oceanic plate sinks, creating a subduction zone. This process forms deep ocean trenches. It also pulls the rest of the plate, causing movement and activity.
Gravity’s role with tectonic plates affects the mantle’s dynamics too. Heat transfer and gravity drive mantle convection. This movement weakens the Earth’s crust, forming rifts and ocean basins.
Together, gravity and plate movement shape our planet. They create mountains, valleys, and trenches. The forces on tectonic plates, led by gravity, keep the Earth changing.

Examples of Subduction Zones
Subduction zones are found worldwide. They show gravity’s effect on plate movement. Here are some notable examples:
- The Andes in South America result from the Nazca Plate sinking under the South American Plate. This process forms the mountains there.
- The Java Trench sees the Australian Plate going beneath the Eurasian Plate. This zone causes many strong earthquakes.
- The Mariana Trench, the deepest ocean part, is created by the Pacific Plate going under the Philippine Sea Plate.
Looking at these subduction zones helps us understand how gravity affects plate movement. It also shows the effects this has on the Earth.
The Significance of Slab Pull in Plate Motion
Slab pull is the main force behind tectonic plate movement. It’s essential for the constant shifting of these plates. This happens when older, colder plates sink, pulling the rest along into the mantle.
This action is like a conveyor belt. The sinking plate drags the rest of the plate. As it sinks, it pulls on the surroundings, moving the whole tectonic plate. This force causes mountains to form, and earthquakes and volcanoes to erupt.
“Slab pull is like the engine driving tectonic plate movement. It’s the force that sets everything in motion and shapes the Earth’s surface over time.” – Dr. Sarah Thompson, Geologist
Other forces also play a role, but slab pull is the most critical. The gravity between the sinking slab and the surroundings makes slab pull powerful. It’s key in moving tectonic plates.
The Role of Slab Pull in Plate Boundaries
Slab pull is clear at convergent plate boundaries, where plates collide. If an oceanic plate meets a continental one, the denser oceanic plate goes underneath. This action, at a subduction zone, causes mountains to rise.
When two oceanic plates meet, the older one subducts under the younger one. Slab pull and gravity together create ocean trenches, volcanic arcs, and earthquakes. These effects come from the motion of the plates.
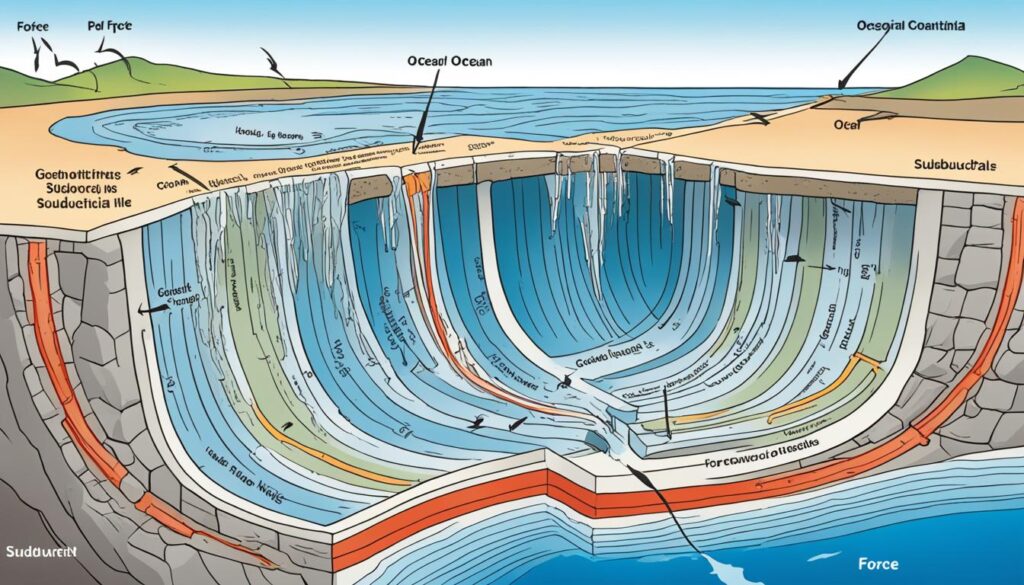
Knowing about slab pull helps us understand Earth’s dynamism. It reveals how tectonic movements shape our planet. This knowledge helps scientists protect communities from dangers like earthquakes and volcanoes.
Conclusion
Tectonic plates move due to several forces like mantle convection currents, ridge push, and slab pull. These forces come from the Earth’s mantle’s heat, from radioactive processes. They work together to change the Earth’s surface. Gravity helps these forces move the plates, which changes our planet constantly.
Learning about tectonic plate movement helps us understand earthquakes, volcanoes, and how new land and oceans form. Knowing how and why plates move lets scientists predict and lessen the damage from natural disasters.
New research and technology improve our knowledge of tectonic plates and their movement. It’s important to keep studying and watching plate tectonics. This helps protect communities in areas where earthquakes happen often. Understanding plate movement gives us important information. This helps us deal with the powerful natural forces that shape our world.
FAQ
What causes tectonic plates to move?
What is the Earth’s interior composed of, and how does it relate to plate movement?
How did the breakup of Pangaea and continental drift contribute to plate movement?
What is the rate of plate movement, and what geological consequences can it lead to?
How does convection play a role in plate movement?
What are the three main forces behind tectonic plate movement?
How does gravity influence plate movement?
What is the significance of slab pull in tectonic plate movement?
Do Winding Roads Signify Tectonic Plate Movement?
Navigating a winding road can be a thrilling experience, but it also raises questions about the geological forces at work. Winding roads are often found in mountainous areas, where tectonic plate movement has created a twisting, turning landscape. So yes, winding roads can signify tectonic plate movement in certain regions.